Eating strategies that incorporate an emphasis on vegetable consumption have been getting more and more attention – ie. paleo, keto, vegetarianism and veganism in the news. This has led to increased availability of plant based substitutes for more traditional ingredients (pasta and rice for example) making it easier than ever to adopt a way of eating that has a focus on more plants. Having a more plant-centric diet can have a lot of benefits to your health when done right, without the need to hunt down any fancy equipment or exotic ingredients to keep your meals interesting.
Many experts point to highly processed, meat-and-fat heavy diets as primary contributors to our skyrocketing health issues. Others point to an increased dependence on nutrient deficient carbohydrate sources and processed foods as the cause. Simply stated, obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and most other chronic diseases can be linked to a lifetime of food choices that aren’t supporting good health. One component of reversing this trend that is supported by science is increasing the volume of plant based foods in our daily food choices. Research shows that a plant based eating strategy is great for the heart, can help combat cancer, and is at the forefront of the war on obesity. Important to note is that not all plant based sources are created equal – while most are better options than heavily processed animal proteins or nutrient deficient carbohydrates:
- fruit and vegetables are not interchangeable. Fruit impacts blood sugar differently than most vegetables so should be consumed in moderation.
- starchy vegetables can have a similar effect as fruit on blood sugar so should also be consumed in moderation and ideally on days when a rigorous workout has been performed.
It’s common to hear from people who have adopted a plant based diet that they feel more energetic, can think more clearly, and can move better with less pain. Plant based foods contain anti-inflammatory compounds which may play a role in these benefits. Plants are full of antioxidants and phytochemicals that simply aren’t available from processed foods or even supplements. The fiber in plant foods is excellent for digestion, and when combined with high quality fats have a high satiety value meaning hunger is experienced less frequently.
The biggest reason the plant based lifestyle has come more into focus is that people are beginning to see improvements in their overall health, their energy levels, and how they feel each day from choosing less processed foods that are closer to their natural state. A fresh tomato is going to be digested differently from ketchup, for example, even if the ketchup is organic. In fact, research shows that a plant based diet that focuses on whole, natural, nutrient dense foods is nutritionally better for you than a diet that is plant based but includes many processed and refined products such as sweetened beverages and many grains.
Is plant-based just a new way of saying vegetarian? Nope! Eating a plant-based diet means focusing on whole, minimally processed foods grown close to nature, where you can recognize each of the ingredients you use. While many vegetarians and vegans will use highly processed items in their meals and think nothing of it, those who eat plant-based choose fresh foods that are full of vitamins and minerals.
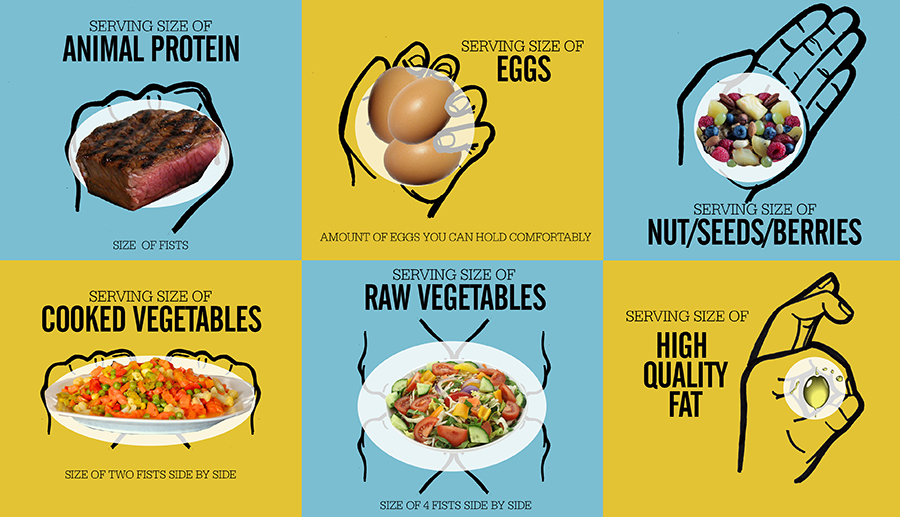
Choosing a plant based diet doesn’t mean that you’re giving up all meats and other animal products. You can and should still incorporate animal proteins if they align with your eating strategy, however, reducing dependence on animal products as the basis of your meals will be beneficial. FiT refers to nutrient density as the foundation of a successful eating strategy. If you consider nutrient density as an equation, it would be nutrients/calories. Macronutrients, which provide all of the calories we consume, come from carbohydrates, protein and fat. Micronutrients are the non-caloric factors in the foods we consume like vitamins, minerals, fibers and phytonutrients. A nutrient dense eating strategy is based on maintaining a high proportion of nutrients to calories (nutrients/calories). Additionally, an optimal strategy incorporates quality and variety, so grass fed meats, pastured chicken and eggs, and wild caught fish are ideal animal protein sources, a wide range of color is a good guide to vegetable consumption and a balance of healthy fats (small, medium and long chain fatty acids) rounds out the equation nicely. The paradigm switch we are recommending here is to think of animal proteins more as a complement or side dish to your vegetable based meal instead of the main and healthy fats as a condiment. A handy ‘quick reference’ using your hand to estimate portion sizes is:
So what does a meal look like? Envision a large serving of mixed roasted vegetables with a side of protein, noodles made from vegetables with meat sauce, a fried egg over a vegetable cake or latke, refreshing salads with creative dressings with grilled chicken, seafood or meat on top, soups and stews are easy, and perfect for the winter months . . . the possibilities are endless! The most common challenge we encounter is prep time to clean and chop vegetables. While fresh is always best, if time constraints prevent fresh from being feasible, most grocery stores offer pre-prepped vegetables – shredded brussel sprouts, chopped broccoli and cauliflower, pre-washed greens and even veggie noodles made from sweet potato or zucchini. These alternatives may be a little pricier, but for some people the trade off in saving time is worth it.
Whether you like to cook simply or you spend hours creating culinary masterpieces, there are plenty of recipes to keep you satisfied with your meals. It’s important to eat a variety of foods to make sure you get all the vitamins and minerals that are necessary for good health. Try to eat foods that are in season for where you live since this will help you to get a broader range of foods in your meals. Shopping for produce at farmers markets or looking for seasonal produce at the grocery store allows you to effortlessly get all the variety you need for excellent health. With so many ways to prepare a variety of vegetables, an additional benefit of eating seasonally is avoiding the sameness that can often make food less enticing. You can enjoy interesting flavors without getting bored while you take the best possible action to maintain robust health and a long life.